在网上大多关于join()与task_done()的结束原话是这样的:
Queue.task_done() 在完成一项工作之后,Queue.task_done()函数向任务已经完成的队列发送一个信号Queue.join() 实际上意味着等到队列为空,再执行别的操作
理解
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
'''threading test'''
import threading
import queue
from time import sleep
#之所以为什么要用线程,因为线程可以start后继续执行后面的主线程,可以put数据,如果不是线程直接在get阻塞。
class Mythread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,que):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.queue = que
def run(self):
while True:
sleep(1)
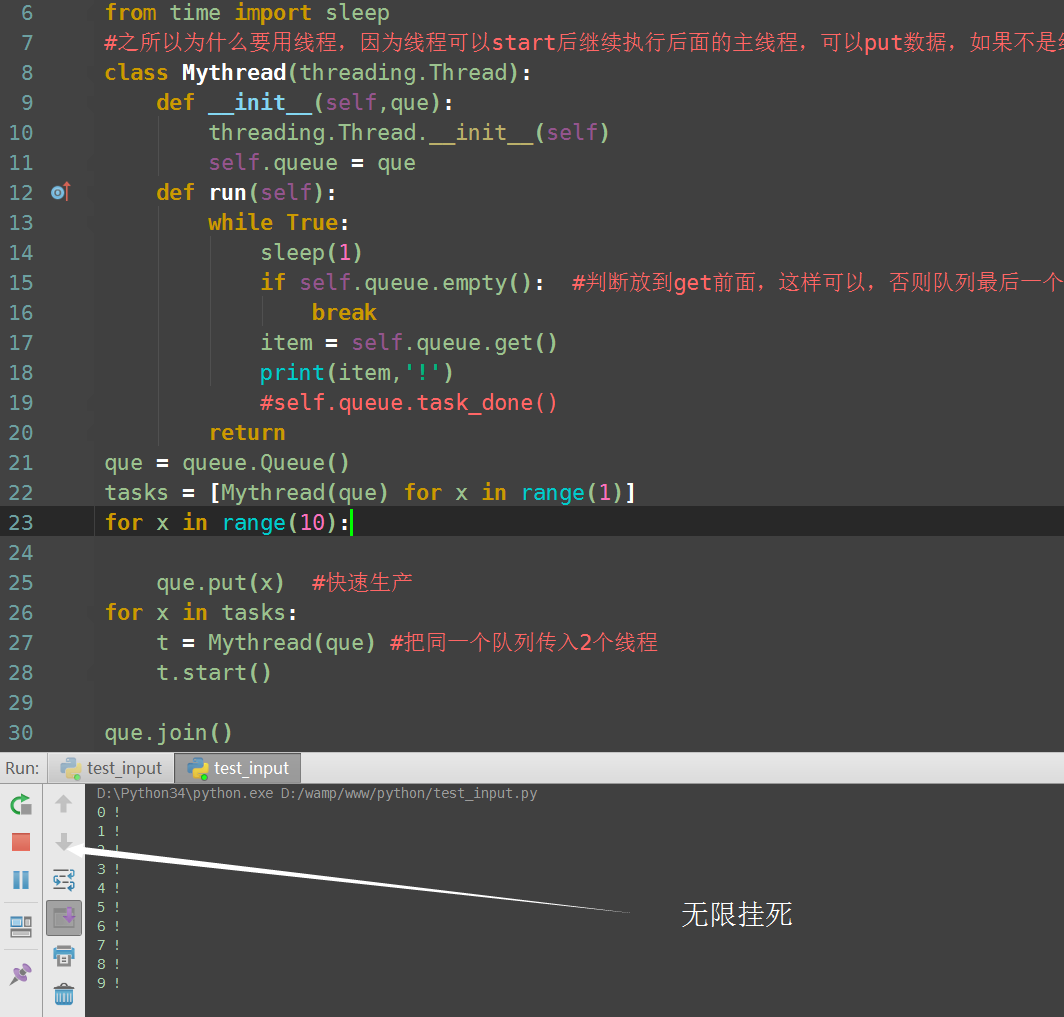
if self.queue.empty(): #判断放到get前面,这样可以,否则队列最后一个取完后就空了,直接break,走不到print
break
item = self.queue.get()
print(item,'!')
#self.queue.task_done()
return
que = queue.Queue()
tasks = [Mythread(que) for x in range(1)]
for x in range(10):
que.put(x) #快速生产
for x in tasks:
t = Mythread(que) #把同一个队列传入2个线程
t.start()
que.join()
print('---success---')
def task_done(self):
'''Indicate that a formerly enqueued task is complete.
Used by Queue consumer threads. For each get() used to fetch a task,
a subsequent call to task_done() tells the queue that the processing
on the task is complete.
If a join() is currently blocking, it will resume when all items
have been processed (meaning that a task_done() call was received
for every item that had been put() into the queue).
Raises a ValueError if called more times than there were items
placed in the queue.
'''
with self.all_tasks_done:
unfinished = self.unfinished_tasks - 1
if unfinished <= 0:
if unfinished < 0:
raise ValueError('task_done() called too many times')
self.all_tasks_done.notify_all()
self.unfinished_tasks = unfinished
快速生产-快速消费
上面的演示代码是快速生产-慢速消费的场景,我们可以直接用task_done()与join()配合,来让empty()判断出队列是否已经结束。 当然,queue我们可以正确判断是否已经清空,但是线程里的get队列是不知道,如果没有东西告诉它,队列空了,因此get还会继续阻塞,那么我们就需要在get程序中加一个判断,如果empty()成立,break退出循环,否则get()还是会一直阻塞。
慢速生产-快速消费
但是如果生产者速度与消费者速度相当,或者生产速度小于消费速度,则靠task_done()来实现队列减一则不靠谱,队列会时常处于供不应求的状态,常为empty,所以用empty来判断则不靠谱。 那么这种情况会导致 join可以判断出队列结束了,但是线程里不能依靠empty()来判断线程是否可以结束。 我们可以在消费队列的每个线程最后塞入一个特定的“标记”,在消费的时候判断,如果get到了这么一个“标记”,则可以判定队列结束了,因为生产队列都结束了,也不会再新增了。 代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
'''threading test'''
import threading
import queue
from time import sleep
#之所以为什么要用线程,因为线程可以start后继续执行后面的主线程,可以put数据,如果不是线程直接在get阻塞。
class Mythread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,que):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.queue = que
def run(self):
while True:
item = self.queue.get()
self.queue.task_done() #这里要放到判断前,否则取最后最后一个的时候已经为空,直接break,task_done执行不了,join()判断队列一直没结束
if item == None:
break
print(item,'!')
return
que = queue.Queue()
tasks = [Mythread(que) for x in range(1)]
#快速生产
for x in tasks:
t = Mythread(que) #把同一个队列传入2个线程
t.start()
for x in range(10):
sleep(1)
que.put(x)
for x in tasks:
que.put(None)
que.join()
print('---success---')注意点:
put队列完成的时候千万不能用task_done(),否则会报错:
task_done() called too many times因为该方法仅仅表示get成功后,执行的一个标记。




![Connectify Dispatch指定程序使用指定网卡[运维神器]](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/1.jpg)
![网站备案流程_网站备案需要什么[简单明了解决备案各种问题]](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/topleft.gif)
![最新BurpSuite 1.7.32 破解版[注册机]下载【无后门版】](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/ee462f76d3e2440f67041f92499c36ae.png)
![php一句话后门的几种变形分析[preg_replace函数]](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/11.jpg)



![[网盘下载] GB/T 23031. 1 — 2022 工业互联网平台 应用实施指南 第一部分:总则.pdf](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/3faee12ec28ab59793fbe1c203b8363f.png)
![[网盘下载] GB/T 41870-2022 工业互联网平台 企业应用水平与绩效评价.pdf](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/4ec246e126c4f3a41d9ced588c790998.png)
![[网盘下载] GB/T 36323-2018 信息安全技术 工业控制系统安全管理基本要求.pdf](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/f6adb0f6fa49a734846c5873d178bfbc.png)
![[网盘下载] GB/T 32919 -2016 信息安全技术 工业控制系统安全控制应用指南.pdf](http://www.vuln.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/da9420e72b7af6bfb4fa273884dcefc1.png)

 云悉指纹
云悉指纹